The Science of Ageing
Ageing is a complex, natural process driven by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
While we can’t stop time, science has made great strides in understanding the biological mechanisms behind ageing, giving us the tools to slow it down and improve our quality of life as we age.
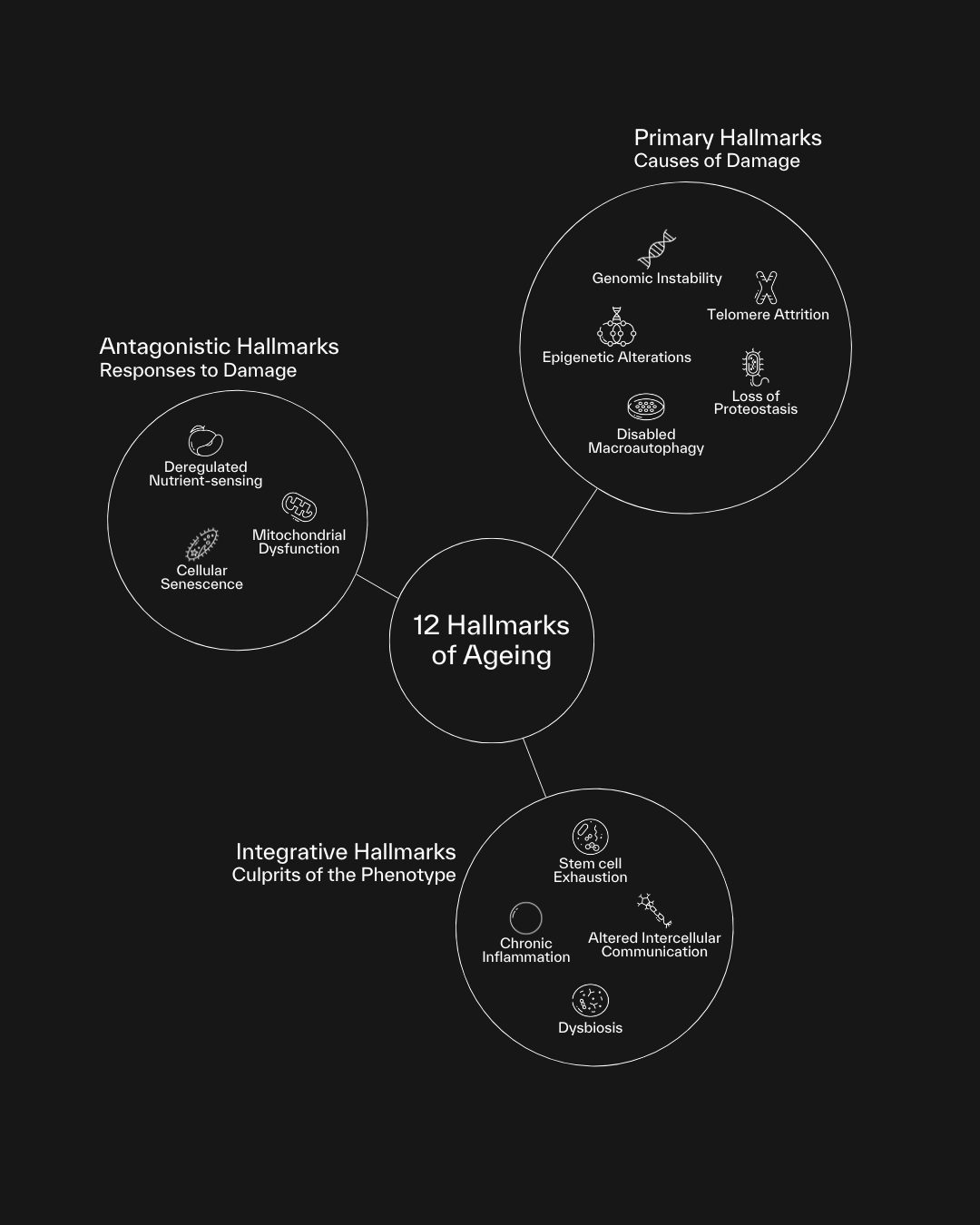
12 Hallmarks of Ageing
The 12 Hallmarks of Ageing are biological processes identified by researchers as key drivers of ageing. These hallmarks act as the underlying mechanisms that lead to the physical and functional decline we experience as we grow older. By addressing these hallmarks, we can slow down the ageing process, prevent age-related diseases, and extend both our lifespan and healthspan.
1. Genomic Instability
Your DNA is like the blueprint for every function in your body, but over time, it can become damaged by various internal and external factors.
Think of it as wear and tear from everyday life — exposure to sunlight, pollution, chemicals, and even the natural processes inside your body can cause tiny breaks or changes in your DNA. These changes, or mutations, can build up over time, leading to diseases like cancer or accelerating the ageing process.
Protecting your DNA means preserving the integrity of your cells, which helps maintain overall health and reduces the risk of age-related illnesses.
2. Telomere Attrition
Telomeres are like the protective caps on the ends of your shoelaces — they prevent your chromosomes from fraying or sticking together when cells divide.
Every time a cell divides, these telomeres get a little shorter, which is a natural part of ageing. However, when they become too short, cells can no longer divide properly, leading to cell ageing or death.
This shortening process accelerates ageing and increases the risk of age-related diseases. Keeping your telomeres longer helps your cells stay younger, supporting overall vitality and reducing the risk of conditions like heart disease or cognitive decline.

3. Epigenetic Alterations
While your genes are fixed, how they are expressed can change based on your lifestyle, diet, and environment.
Imagine your genes as a series of switches that can be turned on or off, affecting how your body functions. Ageing involves changes in these switches, which can lead to health problems or accelerated ageing.
However, you have the power to influence your gene expression through the choices you make every day — from what you eat to how you manage stress. Positive changes can promote healthy gene expression, helping you stay healthier and younger for longer.
4. Loss of Proteostasis
Proteins are the building blocks that keep your cells functioning properly, like tiny workers carrying out essential tasks in your body.
As you age, these proteins can become damaged, misfolded, or accumulate in the wrong places, leading to cellular dysfunction and diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s.
Maintaining protein health — or “proteostasis” — means ensuring that proteins are produced, folded, and cleared away correctly. This balance is crucial for keeping your cells in good working order, which in turn supports overall health and longevity.
5. Disabled Autophagy
Autophagy is like your body’s natural recycling system, where damaged cells are cleared away, and new ones are generated.
This process slows down with age, leading to the accumulation of cellular debris that can cause dysfunction and accelerate ageing.
Boosting autophagy helps keep your cells clean, functional, and youthful, supporting overall health and longevity.
6. Deregulated Nutrient Sensing
Your body relies on a network of sensors to detect and respond to nutrients, much like the way a thermostat regulates temperature in a room. These sensors play a critical role in managing metabolism, growth, and energy.
However, as you age, this nutrient-sensing system becomes less efficient, leading to issues like weight gain, insulin resistance, and reduced energy levels.
Keeping these sensors properly tuned through diet and lifestyle helps maintain metabolic balance, supports healthy ageing, and reduces the risk of metabolic diseases like diabetes.
7. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria are the tiny power plants in your cells that produce the energy needed for all bodily functions. As you age, these power plants can become less efficient and produce more harmful by-products called free radicals.
This decline in mitochondrial function can lead to fatigue, muscle weakness, and a host of age-related diseases.
Supporting mitochondrial health is essential for maintaining your energy levels, mental clarity, and overall well-being, helping you stay active and vibrant as you age.
8. Cellular Senescence
Cells in your body are designed to divide, grow, and then die when they’re no longer needed — like a recycling system. But some cells become damaged and refuse to die off; instead, they enter a state called senescence.
These “zombie cells” linger in your body, secreting harmful substances that cause inflammation and damage surrounding healthy cells.
Clearing these senescent cells helps reduce inflammation, rejuvenate tissues, and promote healthier aging, leading to better overall health and reduced risk of age-related diseases.
9. Stem Cell Exhaustion
Stem cells are like the body’s repair and maintenance crew; they can turn into different types of cells to replace damaged ones, helping your body heal and regenerate.
As you age, your stem cells become less effective, reducing the body’s ability to repair itself and maintain tissue health.
Rejuvenating your stem cells helps keep your body’s repair systems functioning well, which is essential for maintaining youthful tissues, quicker recovery from injuries, and overall vitality.
10. Altered Intercellular Communication
For your body to function smoothly, your cells need to communicate effectively, like a team working together toward a common goal.
As you age, this cellular communication can become disrupted, leading to chronic inflammation, reduced immune function, and other health issues.
Maintaining healthy cell communication helps your body manage stress, repair damage, and stay balanced, promoting a longer, healthier life.
11. Chronic Inflammation
Chronic, low-level inflammation, often called “inflammaging,” is like a slow-burning fire in your body that damages tissues and accelerates ageing.
This inflammation can be triggered by factors like stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, or even undetected infections.
Reducing chronic inflammation is crucial for protecting your health, reducing the risk of age-related diseases, and promoting longevity.
12. Dysbiosis (Microbiome Disturbance)
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and metabolic health, but as we age, its balance can be disrupted by poor diet, stress, medication use, and lifestyle factors—a condition known as dysbiosis.
This imbalance weakens the gut barrier, increases inflammation, and contributes to metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive decline. A diverse and well-balanced microbiome is essential for nutrient absorption, immune resilience, and overall vitality.
Addressing dysbiosis through diet, probiotics, prebiotics, and gut-supportive habits can restore microbial balance, enhancing both longevity and overall well-being.
As we age, these biological processes become less efficient, leading to the gradual decline in physical and cognitive functions.

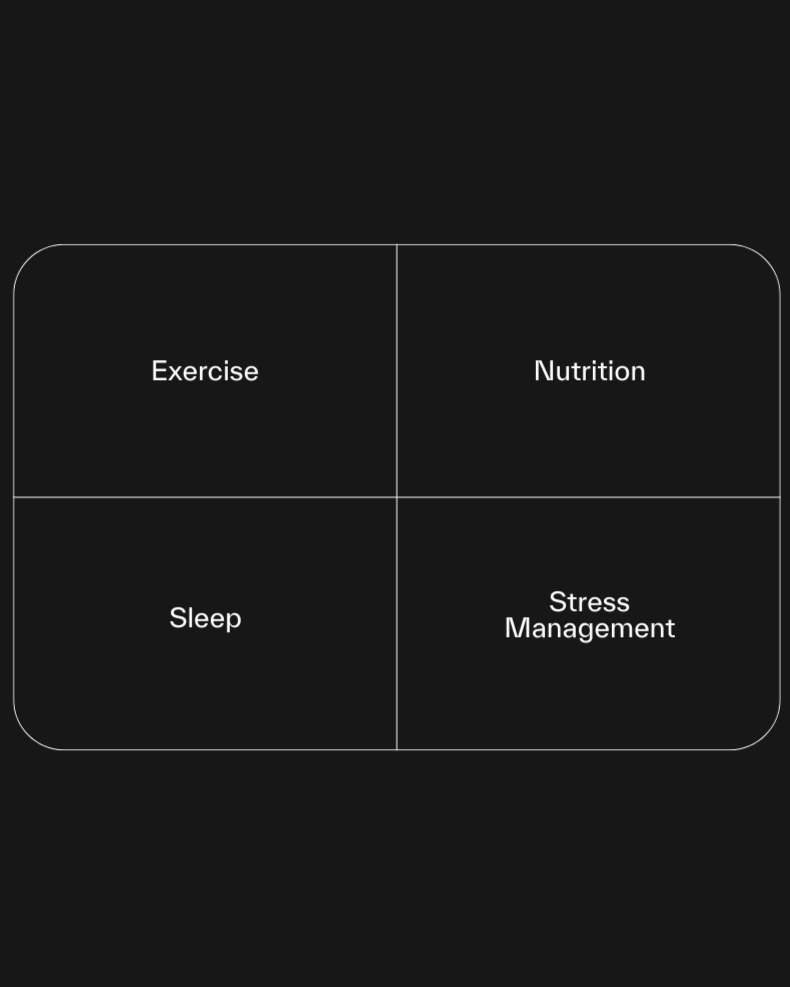
We Utilise Preventive Care to Help You Take Control.
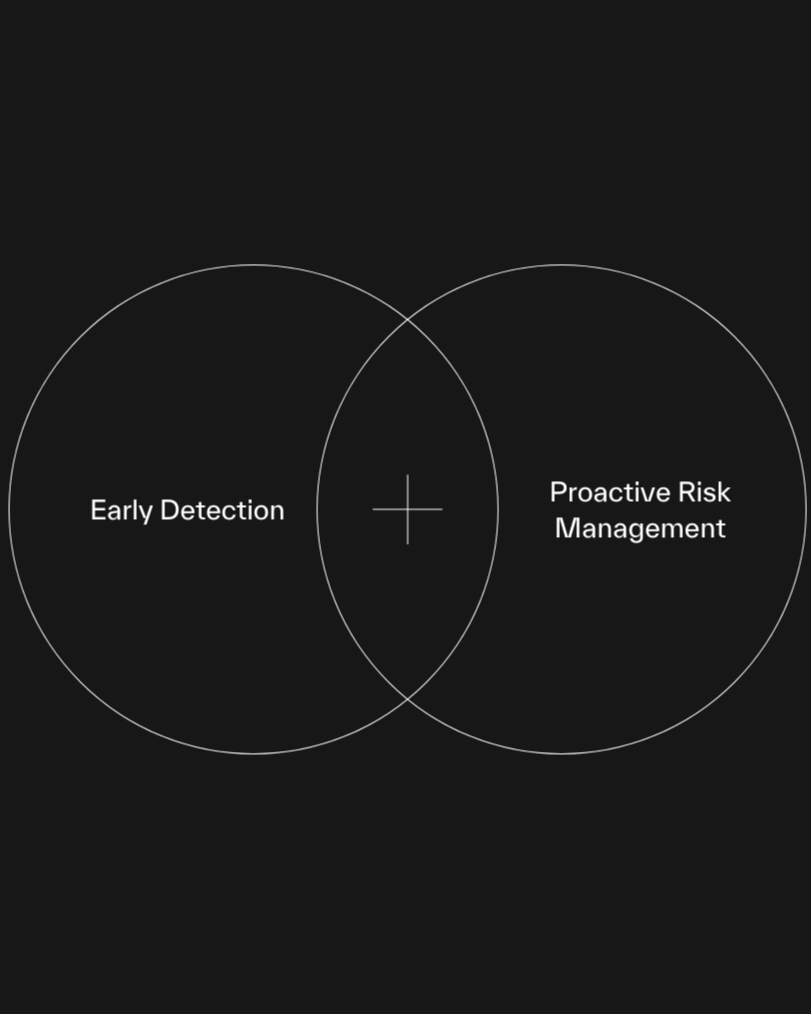
Preventive care is the key to ageing well. Rather than waiting for health problems to arise, taking a proactive approach allows you to maintain optimal health as you age.
Through early detection of health risks, regular monitoring of biological markers, and targeted interventions, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing age-related conditions.
Introducing:
Alpha Vitality's
Vitality
Blueprint
Our Three Pillars
Designed to optimise your Healthspan
Longevity is more than just living a long life—it’s about living well, maintaining vitality, and thriving in good health throughout your years. While many of us seek to extend our lifespan, the true goal of longevity is to increase the years spent in good health, free from chronic diseases or debilitating conditions. This is what we call healthspan—the number of years you live in a high-functioning, healthy state.
What the Experts Say

Dr. David Sinclair - Harvard Medical School
"Only 20 percent of our longevity is genetically determined. The rest is what we do, how we live our lives and increasingly the molecules that we take. It's not the loss of our DNA that causes aging, it's the problems in reading the information, the epigenetic noise."